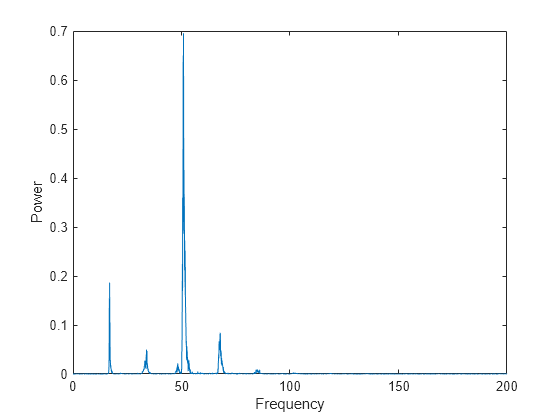
If four out of the possible n frequencies are on then each frequency should have 1 4th of the power of the whole signal again ignoring the noise floor endgroup dan sandberg jan 11 13 at 17 53.
Estimate noise floor of spectrum.
A spectrum analyzer s noise floor has two components.
Characterization of the frequency content of noise using the power spectral density.
Ignoring noise and channel effects each frequency is either at maximum or at the noise floor.
The amplitude of the thermal noise energy is given by the product of three parameters ktb where.
The trick to noise spectrum analysis is that many sample power spectra squared magnitude ffts must be averaged to obtain a stable statistical estimate of the noise spectral envelope.
The total power in the resolution bandwidth at each frequency point.
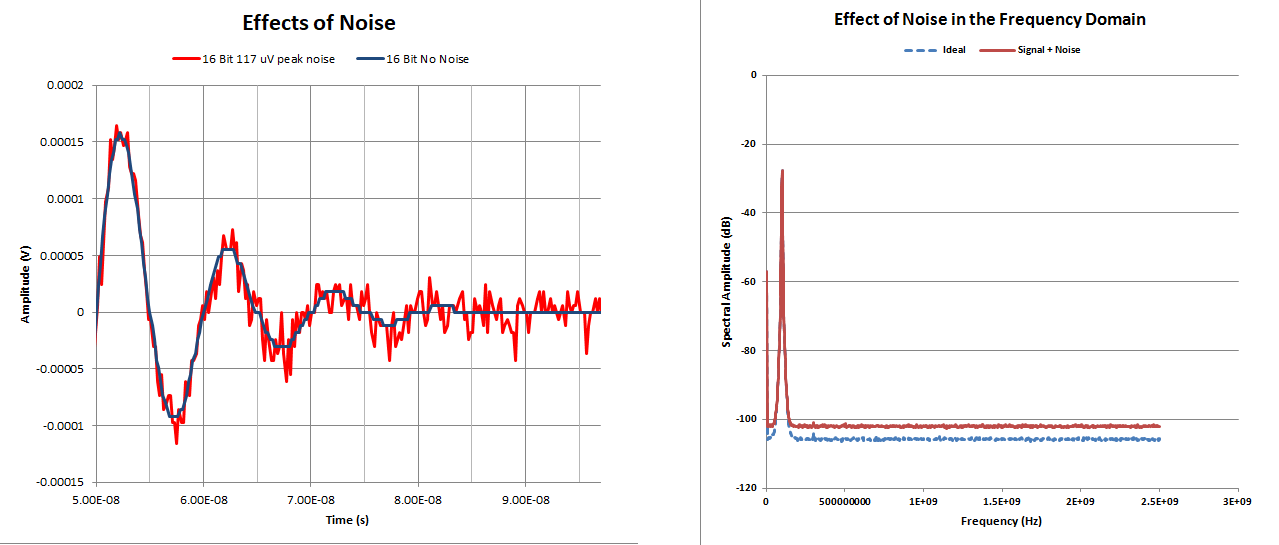
The spectral estimate corresponding to the rectangular window has the expected noise floor but the spectral estimate using the hann window has a noise floor that is about 2 dbm higher than expected.
In the improved mcra approach cohen 2003.
The noise estimate however lags by at most twice that win dow length when the noise spectrum increases abruptly.
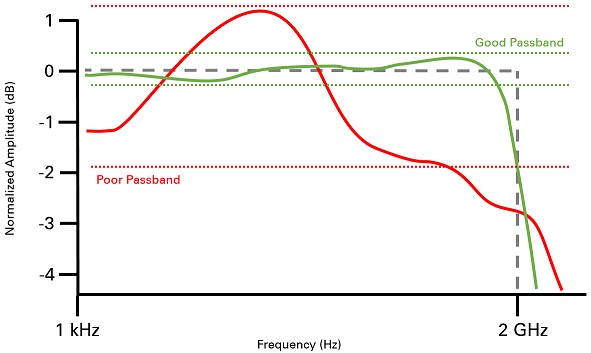
If the noise floor is changing as you change bandwidths it implies that one is measuring power spectrum i e.
More instructional engineering videos can be found at http www enginee.
The reason for this is that the spectral estimate is compute at 512 frequency points but the power spectrum is integrated over the rbw of the.
If for example we wanted to determine the noise floor from 0 to 1 ghz would it be best to run a sweep using a full 1 ghz span or would it be better to pick various frequency ranges with smaller spans.
This is the essence of welch s method for spectrum analysis of stochastic processes as elaborated in 6 12 below.
These regions are found by comparing the ratio of the noisy speech to the local minimum against a threshold.
Noise estimate by tracking the noise only regions of the noisy speech spectrum.
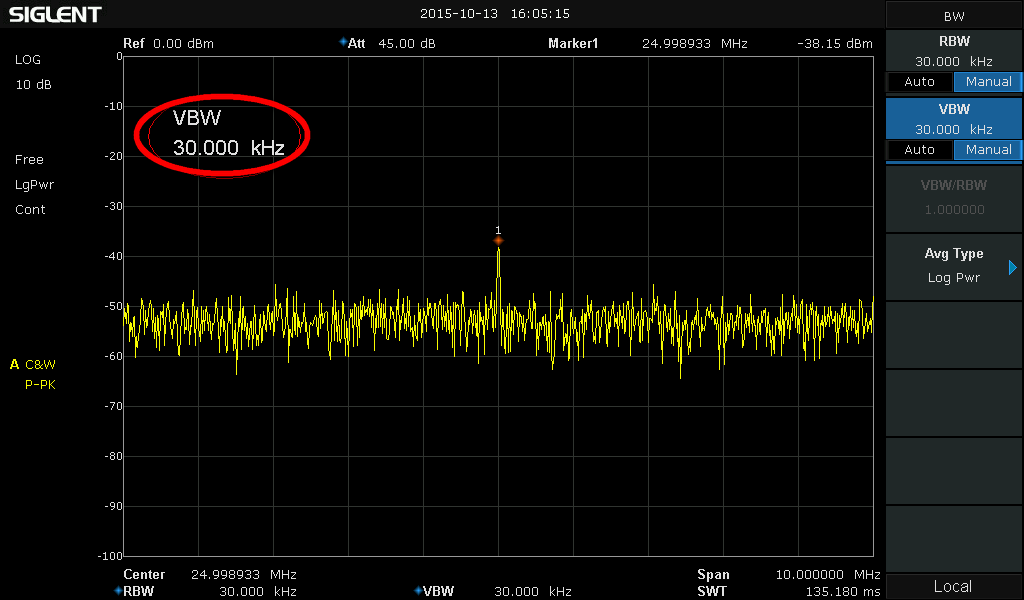
With a spectrum analyzer what is a good method for determining the local noise floor in the lab area around the spectrum analyzer.
Similarly a noise like signal will appear 3 db above the noise floor.
Consequently the apparent noise level will change with rbw whether one is measuring the noise of a device under test or the instrument.
Johnson nyquist noise thermal noise johnson noise or nyquist noise is the electronic noise generated by the thermal agitation of the charge carriers usually the electrons inside an electrical conductor at equilibrium which happens regardless of any applied voltage thermal noise is present in all electrical circuits and in sensitive electronic equipment such as radio receivers can.